Elipsometry

Oferujemy gotowe systemy jak i komponenty
Elipsometr 2-MGEM

Elipsometr jest szybszy, dokładniejszy i zbiera znacznie więcej danych niż poprzednie techniki pomiaru współczynnika anizotropii optycznej.
Modulatory fotoelastyczne są często wykorzystywane w aplikacjach elipsometrycznych i używane w ramieniu generującym stan polaryzacji, ramieniu analizującym stan polaryzacji lub w obu, w zależności od konkretnych elementów macierzy Muellera, które należy zidentyfikować. Elipsometr, który wykorzystuje dwa PEM, jest w stanie zmierzyć wszystkie 16 elementów Mueller Matrix, w tym 4 pomiary anizotropowe.
PEM mogą być używane przy długościach fal DUV, widzialnych i NIR. Prawidłowy dobór detektorów, polaryzatorów, opcji PEM i demodulatorów ma kluczowe znaczenie dla wykrywania niewielkich poziomów elipsometrycznych zmian polaryzacji, które mogą wystąpić.
Pakiety rozwiązań elipsometrycznych mogą obejmować:
- Jeden lub dwa PEM
- Fotodioda lub detektor PMT
- Laser lub inne źródło światła
- Demodulacja wzmacniacza blokującego lub karty przechwytującej przebiegi
- Polaryzatory
- Powłoki antyrefleksyjne
Opracowany we współpracy z Oak Ridge National Laboratory nowy instrument pogłębia wiedzę na temat paliw jądrowych czwartej generacji i charakterystyk polaryzacji odbiciowej.
System pomiaru współczynnika anizotropii optycznej 2-MGEM jest mikroskopem polaryzacyjnym o normalnym zdarzeniu, przeznaczonym do pomiaru próbki matrycy Muellera i jest zdobywcą nagrody 2008 R&D 100 Award.
2-MGEM Optical Anisotropy Factor Measurement System
Developed in cooperation with Oak Ridge National Laboratory, a new instrument is advancing the understanding of 4th Generation nuclear fuels and reflected polarization characteristics.
The 2-MGEM Optical Anisotropy Factor Measurement System is a normal-incidence polarization reflection microscope designed to measure the sample Mueller matrix and is a 2008 R&D 100 Award Winner.
This system is designed specifically to evaluate the Optical Anisotropy Factor (OPTAF) of cross sections of TRISO nuclear fuel pyrocarbon layers. Other possible material characterizations include measuring Mueller matrix elements of other crystals, carbon compounds, and thin film coatings (e.g. surfacedeposition films) at normal incidence.
The 2-MGEM can also measure retardation (d), circular diattenuation (CD) and the polarization factor (ß). These parameters are not measurable using older techniques, since those techniques do not incorporate a compensating optical element.
Measuring TRISO:
Understanding the preferential orientation of the graphite in TRISO inner pyrocarbon (IPyC) and outer pyrocarbon (OPyC) coating layers can identify formation orientation issues that will lead to premature failure of the containment.
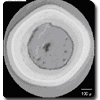
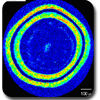
Advantages of measuring TRISO particles with the Hinds Instruments 2-MGEM:
No sample rotation is needed.
2-MGEM data is taken as a function of x- and y- position, making it possible to construct an image of the various measured parameters. All of the previous techniques are only able to measure at single points.
Optical resolution <4 microns
The 2-MGEM measures 8 parameters, which can then be reduced to the diattenuation N and the principal direction. The quantities N and cannot be measured simultaneously using any of the older techniques.
The 2-MGEM measures each of the 8 parameters to ~0.001; previous measurements of OPTAF were accurate to ~0.01. The 2-MGEM is 10 times more accurate. This accuracy is critical because the variations in the diattenuation from processing conditions are often as small as 0.002.
Masz pytania ?
Dostawcy







